Market research is the methodology that helps businesses know their customer and their competitors more in-depth. Although every company would love to have that insight, I have often asked, whether small businesses and early-stage startups need market research or if they should focus their limited resources on other important areas. In this article, I will try to discuss different opinions and provide my own perspective.
What is Market research?
Market research is the process of gathering information about a market to understand its size, growth, and profitability. The process of creating a market research report is to analyze the current state of a given industry, including market size and segmentation, key players, and growth opportunities or threats. The report then presents an overview of future market opportunities for the industry or company based on various forecasts for both macro-level trends and micro-level trends. Finally, the report presents recommendations for how to maximize success in the industry.
A market research strategy is an essential part of every business’s foundation. It is a vital component in developing any business plan and should be considered as important as financial projections or marketing plans.
In the first part of this article, I will discuss what exactly is market research in general and how it can be done efficiently. Then, I will continue with whether it could be done in a startup or not.
What are the benefits of market research?
Market research provides a lot of benefits for businesses, including understanding customer needs, knowing their competition, understanding the trends in the industry, predicting future trends, and much more. It can provide benefits for retailers, manufacturers, and suppliers. Market research is conducted to understand consumers’ demands, abilities, and behavior patterns.
Through market research. consumers can be marketed to on an individual level or a group basis. Market Research has different approaches such as:
-
In-depth explorations of customer needs
-
Competitive analysis
-
Study of current trends in the industry including changes in demographics and technology
-
Forecasting what the future holds for customers as well
Segmentation
Segmentation is a process of dividing the market into small groups of customers. It helps marketers to identify the specific and detailed characteristics of their target market and then cater to them accordingly.
In order to segment their customers, marketers use analytical tools like surveys, polls, and questionnaires. They also use secondary data like purchasing patterns, browsing history, etc. To understand more about their customers, marketers use segmentation at demographic and behavioral levels.
Targeting
Marketing is all about targeting and the more specific the targeting criteria, the better. Predictive targeting is a method of market segmentation that uses data to predict future customer behavior. It’s not just about who they are and what they buy, but also when they buy it. The more data you have on your potential customers, the easier it will be to target them with a specific marketing message.
There are many schools of thought on how to choose a target, but I always consider these factors:
- Segment size: to make sure it would be a profitable segment for the company
- Expected growth: to consider in the life cycle of marketing strategy
- Competitive position: which will be directly translated to your acquisition cost
- The cost to reach: some segments are more expensive to reach due to limited communication channels
- Compatibility: ensuring that the selected segment is aligned with the overall company goals and objectives
Positioning
A company’s market position is determined by the perception of its customers and potential customers. Market position can be changed through the use of marketing and advertising. Marketers need to know how to choose the right positioning for their product or service in order to increase brand awareness and generate more sales.
The market position of a company is largely dependent on its branding strategy and its competitors. A company’s brand image will determine what kind of perception they have in the eyes of consumers, which then influences how they are positioned in the marketplace.
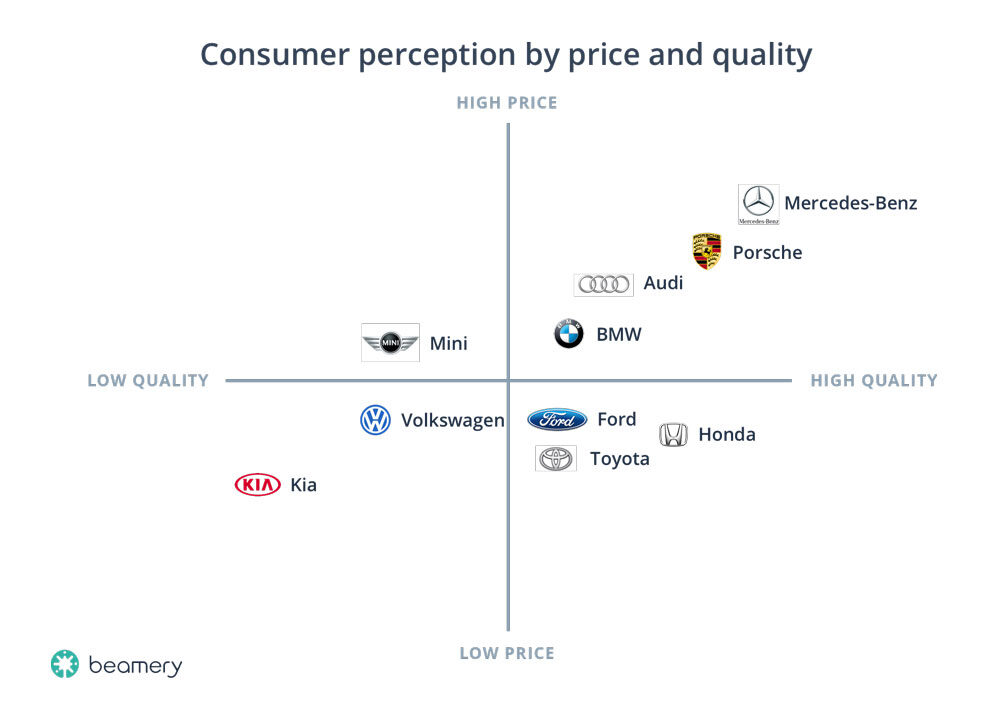
One of the most used tools to visualize positioning is perceptual mapping. In this method, each brand is located in a graph with two axes representing the two major attributes, customers consider when choosing among them. Here is an example from the car manufacturing industry based on two factors: price and quality
Buyer Persona
A buyer persona is a marketing tool that helps businesses understand who their customers are and what motivates them. A buyer persona is a fictional character created to represent a segment of the customer population. It includes demographic, psychographic, and behavioral data about the segment’s members.
This character helps marketers understand their target audience better so they can create marketing messages that resonate with these specific groups. Also, it helps internal communication about the target market way easier as it is like the whole company tries to sell to a single person who everybody knows in-depth.
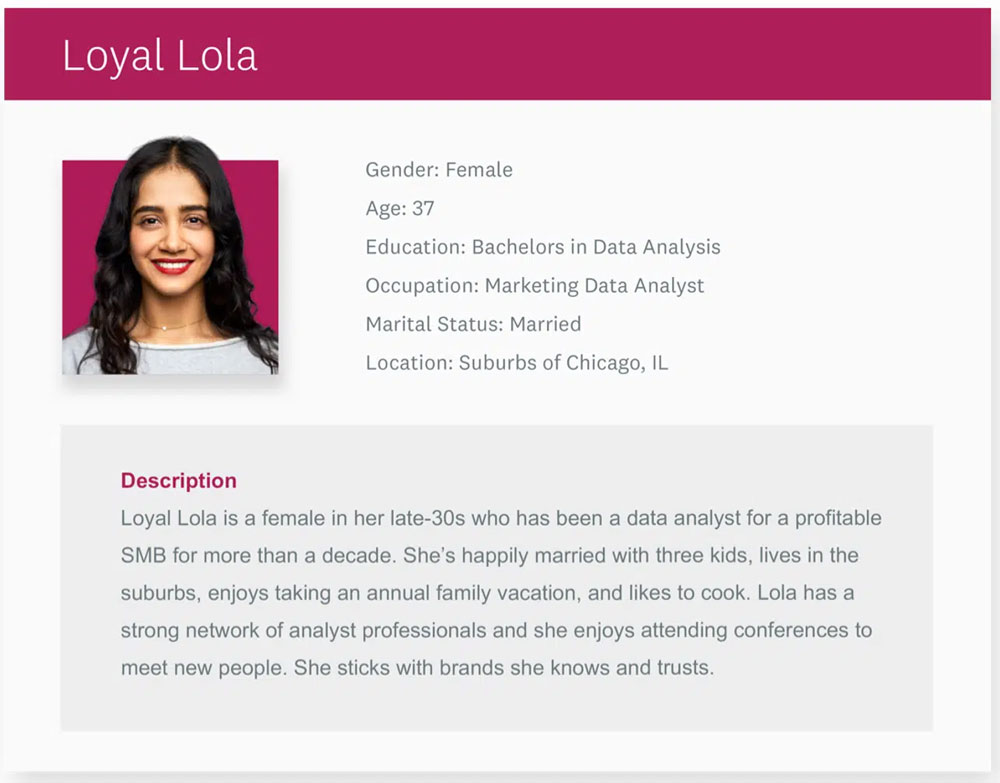
Example of Persona: A Brand-Loyal Suburban Home Cook
This example from Survey Monkey of a buyer persona breathes life into a fictional data analyst. We learn about her education, where she lives, and her interests and passions — she likes to cook and travel, values her relationships, and is brand-loyal.
How would your company’s prototypical client impact your marketing strategy or product offerings if this were your company? Having a clearly defined buyer persona helps frame every decision you make.
Can startups afford market research?
After learning what is market research, why is it important, and how it is usually done, entrepreneurs, start asking themselves can we afford to run that process? I believe considering the nature of a startup which is dealing with plenty of unknowns on a daily basis and the limited budget for test and learning, unlike more established companies, the right question to ask is how a start-up can afford NOT run the market research. So, here I will provide solutions for early-stage companies to gather data about their target market and turn them into insights.
How can a startup run market research?
Considering the specific characteristics of each market and industry, a startup can choose the right methods and decide to what extent they want to run their test, For example, most online businesses start gathering data from their potential customers very early by implementing analytical tools like, google analytics and Hotjar. However, other offline companies with B2B models might struggle to learn about their customers and competitors before attending many meetings. Although, there is no one size for all model, based on my experience these two methods could be a great starting point for small businesses to get insights into their target market.
Important: I cannot emphasize more on remembering to avoid friends and family members in the market research process for your product, service, or company in general. I know many entrepreneurs who got mislead by their friends and family with their biased opinions out of kindness. Believe me, in this stage only thing you need, is brutal feedback from people who are your potential customer.
Focus Groups
A focus group is a small group of people selected based on their specific shared characteristics, to take part in a discussion for your market research who are usually either your current or potential customers. Focus groups are one of the main techniques of qualitative research, which delves into a wide variety of phenomena. These include motivations, attitudes, the reasoning behind actions, opinions, sentiments, and beliefs.
Although it might not be statistically valid and reliable to run just a couple of focus groups with few people, startups could benefit a lot from the insight from this method. These insights could be tested through A/B tests and other tools on larger scales.
Secondary data: Third-Party sources
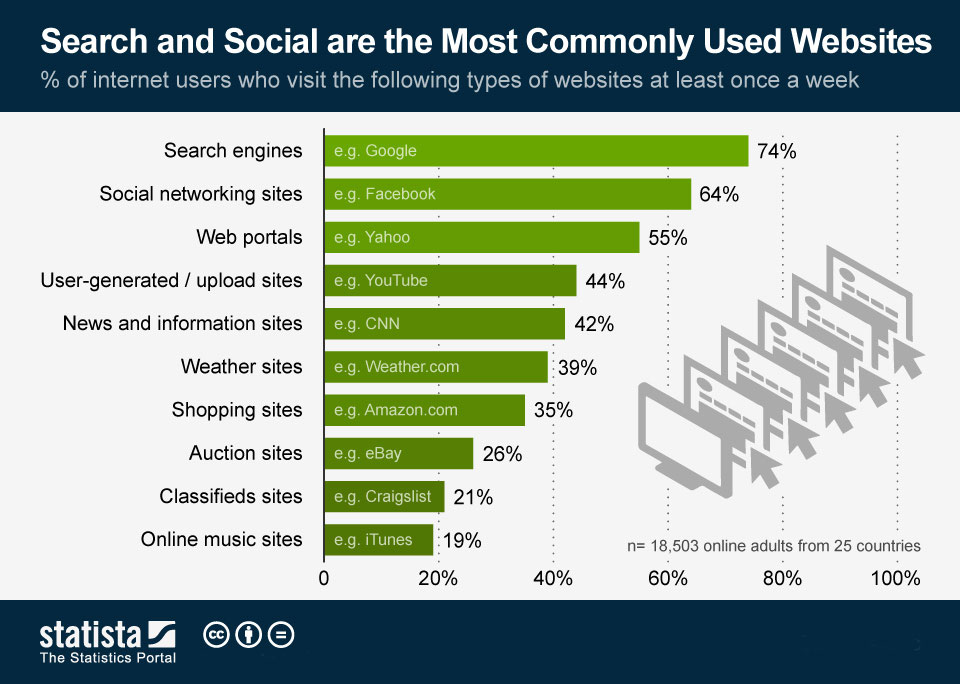
Secondary data is the data that has already been collected and is readily available. This data is pre-existing public information, for instance, the data shared in public sources like magazines and newspapers, government statistics; commercial sources like paid industry reports; and internal sources i.e. the market data that the organization already has in-house. Here is an example from Statista one of the most reliable sources of secondary data.
The procedures that these sources use to analyze the data collected most of the time include product testing, market segmentation, advertising testing, usability testing, key driver analysis for loyalty and satisfaction, awareness and usage research, and pricing research.
To use these resources, you should be searching both online and offline sources and sometimes be creative. For example, one of the ways I used to search for data about the target market in my startups was to read the competitors’ Crunchbase pages and look for signals and news. There were plenty of articles discussing my competitors’ market size, value, and characteristics which were invaluable information on the path to crafting my market research document, all for free!